Accessing Cloud Dashboards¶
To access cloud management dashboards,
With Zenko installed on a Kubernetes cluster, open a command line on your local workstation and enter
kubectl proxyfrom your local Kubernetes repo. This opens a kubectl proxy session that enables you to access dashboards. Leave this process running.Make sure the path to the cluster’s configuration file is exported to the environment. For a MetalK8s installation, open another command-line interface and export the path to the configuration file with the following command:
$ export KUBECONFIG=`pwd`/inventory/<cluster-name>/artifacts/admin.conf
Open a browser, and enter the Kubernetes dashboard at: http://localhost:8001/api/v1/namespaces/kube-system/services/https:kubernetes-dashboard:/proxy/#!/overview?namespace=default
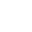
Log into your Kubernetes installation.
Tip
If you used MetalK8s for your Kubernetes installation and want to use Basic authentication, look for your user name and password in the inventory file. The default location is:
/[...]/metalk8s/inventory/<cluster name>/credentials/kube_user.creds
The Kubernetes dashboard displays:
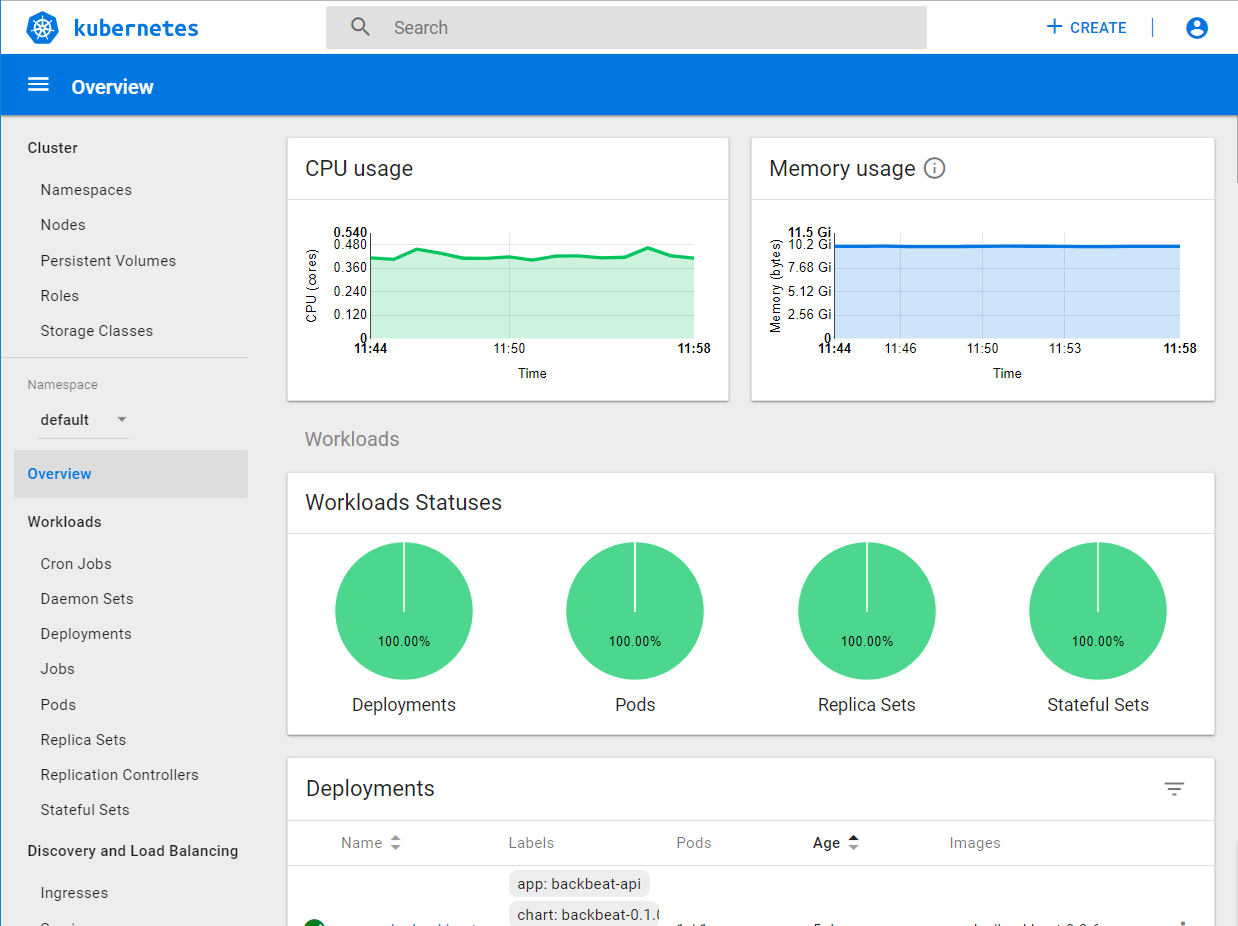
For MetalK8s deployments, if the Kubernetes dashboard is visible, you can also access the other Kubernetes-dependent services Zenko offers as part of its default stack.
Troubleshooting Cloud Dashboards¶
To operate, Zenko ties together several systems, many of which are not part of the core Zenko product. Because of this, describing every possible configuration impossible; however, these are the main points of failure when accessing cloud dashboards.
The dashboards to control, monitor, and adjust your Kubernetes cluster and Zenko instance are available when the following conditions are met:
- The cluster is operating.
- The appropriate ports on the cluster are open.
- Your local environment has access to the admin.conf file, which is also stored on the cluster.
- Cluster ingress is configured correctly and identified accurately on the local machine.
- There is an open kubectl proxy session.
- You have the correct credentials.
Cluster Is Up¶
To be sure the cluster is operating, check out the management interface and make sure all nodes of your cluster are up and running. Check to see that all nodes are live, and that each node has an attached and running storage volume. You may be able to diagnose problems by sending kubectl commands to the cluster. For a complete listing of active pods and their current status, enter:
$ kubectl get pods
To find backbeat-api status, enter:
$ kubectl get pods -l app=backbeat-api
The filtered result is:
zenko-backbeat-api-787f756fb7-8hwh4 1/1 Running 6 2d
If you are concerned about a particular node’s health, enter:
$ kubectl get nodes
Ports Are Open¶
Make sure each node is configured with ports 6443, 80, and 443 open and accessible to incoming traffic from your local machine.
KUBECONFIG Environment Variable is Correctly Set¶
If you are in the make shell virtual environment from which you
created a MetalK8s deployment, the appropriate environment variables are
already set. If you can’t enter this virtual environment or are using
another Kubernetes, find the admin.conf file, which was generated with
your Kubernetes setup. Your local machine must know where to find this
file.
To see whether this is set properly in your environment, enter
$ env | grep KUBE
If the KUBECONFIG environment variable is set, the response shows a path; for example:
KUBECONFIG=/home/username/metalk8s/admin.conf
If KUBECONFIG is not set (that is, the env command shows no result for
KUBECONFIG), you must export the path. Once you find the path to admin.conf,
export it with:
$ export KUBECONFIG=/path/to/admin.conf
The admin.conf in the local client device must match the admin.conf file in the Kubernetes cluster. For MetalK8s, this is defined in the inventory at […]/metalk8s/inventory/<cluster-name>/artifacts/admin.conf and is copied to /etc/kubernetes/admin.conf on deployment.
Windows users may experience trouble if the admin.conf file is installed in a user’s personal directory. Windows may inject a space in the user name, which breaks the path. If you use a Windows machine, make sure admin.conf resides in a path that contains no spaces.
Proxy Is On¶
To access the cloud dashboards, you must open and maintain a kubectl proxy session. Open a terminal, run the following command, and leave it running.
$ kubectl proxy
Starting to serve on 127.0.0.1:8001
Correct Credentials¶
You must have correct credentials to access the Kubernetes dashboard. For MetalK8s deployments, look for Kubernetes credentials in […]/metalk8s/inventory/<cluster-name>/credentials/kube_user.creds. Copy and paste this file’s contents as the password when you log in to the MetalK8s Kubernetes desktop. If you have recently reinstalled a cluster, make sure your browser is not presenting old credentials. Other Kubernetes engines may employ different authentication strategies. For any such problems, request help from the Kubernetes vendor or community you have chosen.