Deleting Objects¶
To delete objects from a selected bucket:
Click the Browser button in the sidebar to open the Multicloud Browser:
Double-click a button to open it:
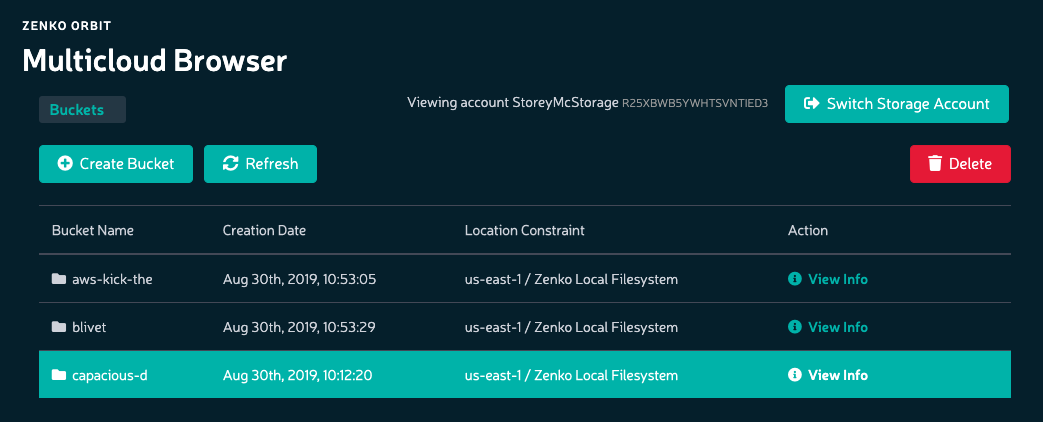
Click the check box next to each object to be deleted. The number of objects to be deleted is indicated in the top bar of the file list.
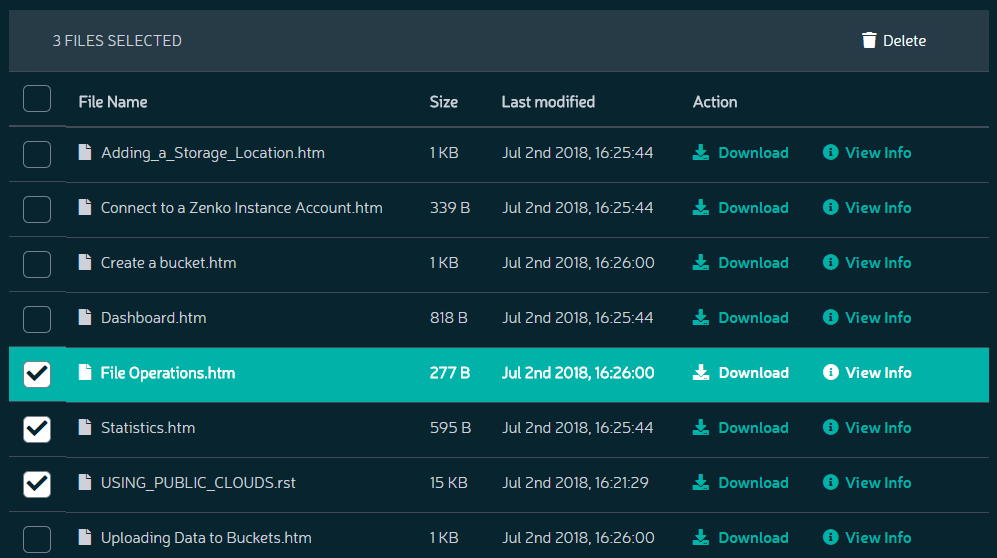
Click the Delete button.

Orbit requests confirmation of the deletion.
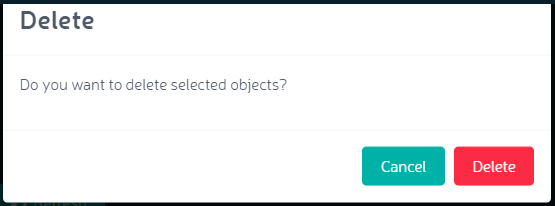
The object is deleted from the bucket.
Important
If versioning is enabled (the recommended configuration for AWS nodes) deleting from the Orbit UI deletes the most recent version of the object only. This results in a condition where the bucket appears empty, but continues to contain previous versions of the deleted object. This prevents the bucket from being deleted, because it is not empty. To completely delete an object and its version history requires entering the CLI commands described below.
Deleting Versioned Objects¶
Deleting versioned objects is difficult because cloud servers are biased towards preserving data. While this is useful, it can become problematic when large numbers of objects are under management (during stress testing, for example).
To completely delete a versioned object, you must issue S3 API commands from the command line.
If you have not already done so, follow the instructions at Zenko from the Command Line to configure one of your nodes to accept AWS S3 CLI commands.
Zenko provides command-line scripts that enable removing versioned objects completely (both removing the object data and its object ID from the namespace).
The cleanupBuckets.js script is available in the s3utils pod.
Run it as follows:
Enable the s3utils pod with:
$ kubectl run s3utils --image=zenko/s3utils:0.5 -it bash
Tip
The s3utils pod is disabled by default. You can also enable it by adding the following to the options file and upgrading your Zenko deployment:
maintenance: debug: enabled: true # An access/secret key to access Zenko that will be used to configure the s3utils pod accessKey: <access-key> secretKey: <secret-key>
Use grep to find the s3utils pod:
$ kubectl get pods | grep s3utils myzenko-zenko-debug-s3utils-7f77f9b5b9-627gz 1/1 Running 0 31m
exec into the s3utils pod:
$ kubectl exec -it myzenko-zenko-debug-s3utils-7f77f9b5b9-627gz bash
Run the cleanup script with:
$ node cleanupBuckets.js <bucket1> <bucket2> ...
On versioned buckets, this script deletes current and archived versions, deletes markers, and aborts any ongoing multipart uploads.
Buckets are cleaned up (emptied of all objects and versions), but not deleted. With all object versions in a bucket thus deleted, you can delete the bucket from the command line with:
$ aws s3api delete-bucket --bucket <bucket-name> --endpoint-url http://<zenko.endpoint.url>
or delete the bucket using the Orbit Multicloud Browser.